Because POTS involves the nervous system, neurologists often play a central role in diagnosis, management, and long‑term care. This article explores how neurologists support POTS patients, what to expect during consultations, and why their expertise is essential for improving quality of life.
Understanding POTS and the Nervous System
POTS is classified as a form of dysautonomia, meaning it arises from dysfunction in the autonomic nervous system. This system controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and temperature regulation. Neurologists specialize in disorders of the nervous system, making them uniquely positioned to evaluate how autonomic dysfunction contributes to POTS symptoms.
The Neurologist’s Role in Diagnosis
Comprehensive Evaluation
Neurologists begin by taking a detailed medical history and performing neurological examinations. They look for patterns of symptoms such as lightheadedness, palpitations, brain fog, and exercise intolerance.
What dietary strategy have you found most helpful for symptom control?
Autonomic Testing
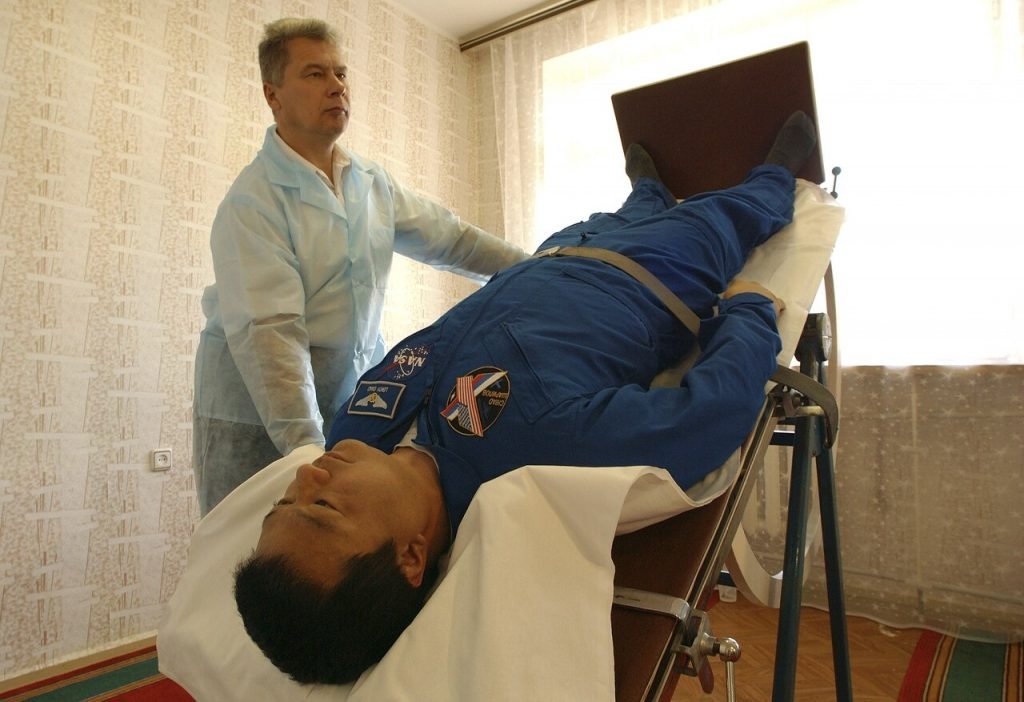
Specialized tests may include tilt‑table testing, autonomic reflex screening, and heart rate variability studies. These help confirm the diagnosis of POTS and rule out other neurological conditions.
Differential Diagnosis
Because POTS shares symptoms with conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome, anxiety disorders, and vestibular dysfunction, neurologists are critical in distinguishing POTS from overlapping disorders.
Neurologists in Symptom Management
Medication Oversight
Neurologists may prescribe or adjust medications that regulate blood pressure, heart rate, and nervous system activity. These can include beta blockers, fludrocortisone, or medications that improve autonomic tone.
Lifestyle Guidance
Beyond prescriptions, neurologists often recommend lifestyle strategies such as increased fluid and salt intake, compression garments, and gradual exercise programs tailored to autonomic stability.
Cognitive and Neurological Support
Brain fog, migraines, and sleep disturbances are common in POTS. Neurologists address these neurological symptoms directly, helping patients manage cognitive fatigue and improve daily functioning.
Collaboration with Other Specialists
Neurologists rarely work in isolation. They coordinate care with cardiologists, primary care physicians, and sometimes gastroenterologists or endocrinologists. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of POTS—cardiac, neurological, and systemic—are addressed.
Neurologists and Long‑Term Care
Monitoring Progress
POTS symptoms can fluctuate over time. Neurologists track changes, adjust treatment plans, and provide ongoing support.
Patient Education
Neurologists empower patients with knowledge about their condition, helping them understand triggers, pacing strategies, and self‑management techniques.
Research and Innovation
Many neurologists are involved in clinical research, offering patients access to emerging therapies and contributing to the broader understanding of POTS.
Practical Tips for Patients Seeing a Neurologist
- Prepare a symptom diary to share during appointments.
- Ask about autonomic testing options.
- Discuss both neurological and systemic symptoms.
- Inquire about lifestyle modifications alongside medications.
- Request referrals to other specialists if needed.

GnarlyTree | PRACTICAL TIPS
Workplace Accommodations for POTS | How to Thrive with POTS at Work
Living with POTS presents real challenges—especially in the workplace, where demands can conflict with physical limitations. Fortunately, with the right strategies and support, individuals can navigate their careers while managing symptoms effectively. This guide explores...
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main role of a neurologist in POTS?
A neurologist evaluates autonomic dysfunction, confirms diagnosis, and manages neurological symptoms.
Do neurologists perform tilt‑table testing?
Yes, many neurologists oversee or interpret tilt‑table tests to diagnose POTS.
Can a neurologist prescribe medication for POTS?
Neurologists often prescribe medications to regulate heart rate, blood pressure, and nervous system activity.
How do neurologists help with brain fog in POTS?
They assess cognitive symptoms and recommend strategies or treatments to improve focus and reduce fatigue.
Do neurologists work with cardiologists for POTS care?
Yes, neurologists collaborate closely with cardiologists to provide comprehensive treatment.
Is lifestyle advice part of a neurologist’s role?
Absolutely, neurologists often recommend hydration, salt intake, compression garments, and exercise plans.
Can neurologists help with migraines in POTS patients?
Yes, they address neurological symptoms like migraines, which are common in POTS.
Do neurologists provide long‑term follow‑up for POTS?
They monitor progress, adjust treatments, and support patients over time.
Final Thoughts
Neurologists play a vital role in the care of POTS patients by diagnosing autonomic dysfunction, managing neurological symptoms, and coordinating multidisciplinary treatment. Their expertise ensures that patients receive comprehensive support for both immediate symptom relief and long‑term management. For individuals living with POTS, partnering with a neurologist can be a crucial step toward improved quality of life, better symptom control, and greater confidence in navigating this complex condition.
By understanding the neurologist’s role, POTS patients can approach their care with clarity, empowerment, and hope.
Have you found that supplementing for any nutritional deficiency helped your symptoms?