Why Exercise is Important for POTS Management
Finding the Best Exercise Equipment for POTS is important. Managing Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome requires a strategic approach to exercise, incorporating tools that promote circulatory stability, heart rate control, and muscle strength. Choosing the right exercise equipment can significantly impact symptom management, allowing individuals with POTS to build endurance, improve mobility, and prevent excessive autonomic stress.
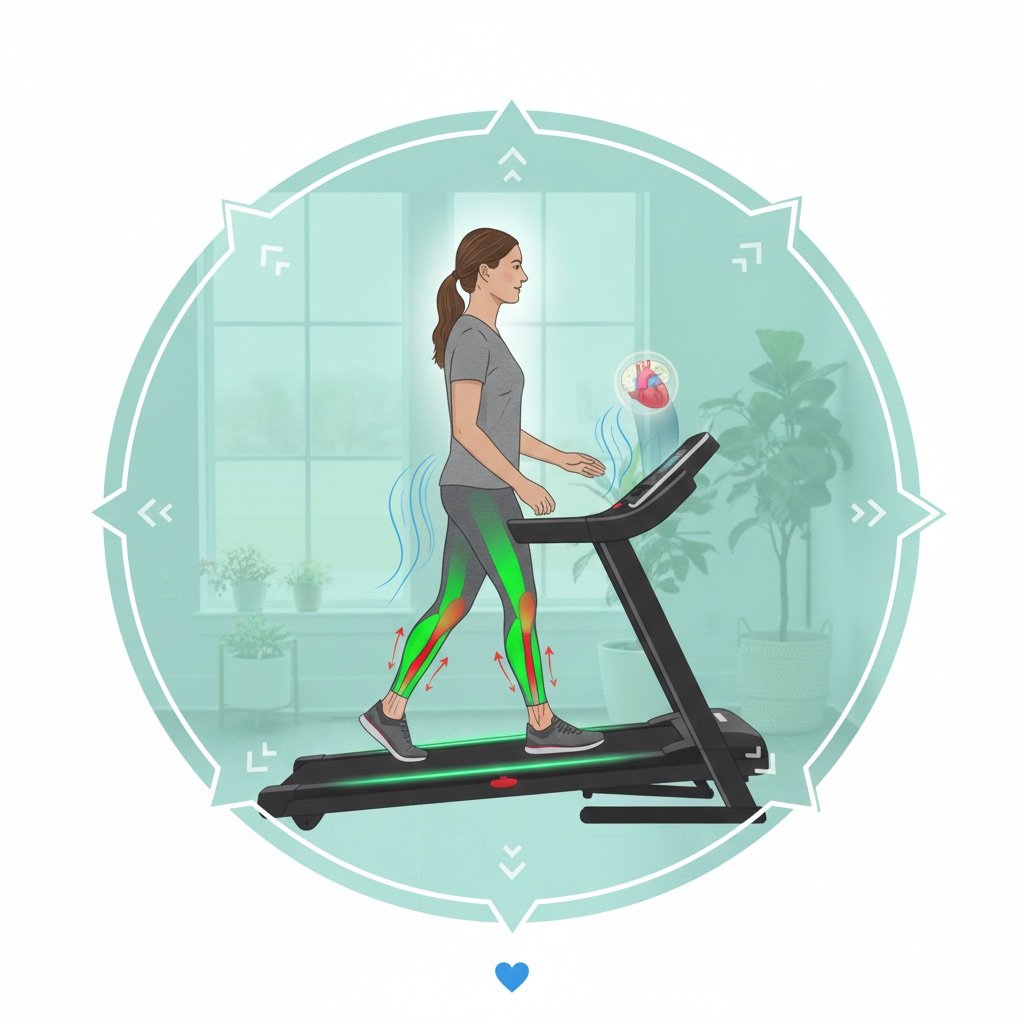
Regular physical activity plays a vital role in strengthening the cardiovascular system, improving blood circulation, and reducing orthostatic intolerance—a key challenge for individuals with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS). Exercise helps condition the body to manage autonomic dysfunction more effectively, promoting better vascular tone and stability.

Strengthening Cardiovascular Function
One of the biggest benefits of exercise for POTS management is its ability to gradually improve heart rate control and enhance blood flow efficiency. Since autonomic dysfunction can cause erratic heart rate fluctuations, introducing structured movement patterns helps condition the cardiovascular system, reducing symptoms over time.
How do you best manage a "POTS bad day"?
Low-impact workouts, such as recumbent cycling, rowing, or resistance training, encourage the heart to adapt more effectively to postural changes, preventing excessive tachycardia spikes that often occur upon standing.
Improving Circulation and Blood Flow
Poor circulation can lead to blood pooling, causing dizziness, fatigue, and difficulty regulating blood pressure. Exercise stimulates circulation, supporting proper blood vessel function while reducing circulatory stagnation.
Since individuals with POTS may struggle with standing exercises, seated workouts allow for better control over blood flow, ensuring a safer progression without overwhelming the nervous system.
Reducing Orthostatic Intolerance
Exercise strengthens vascular tone, helping the body maintain blood pressure stability and reducing lightheadedness when transitioning between positions. By gradually building muscle support, individuals with POTS experience less strain on circulation, allowing for better tolerance of daily movements.
Why Exercise Must Be Approached Carefully
Due to autonomic dysfunction, individuals with POTS must approach workouts cautiously, ensuring that movements do not trigger overexertion or symptom flare-ups. This includes:
- Starting with low-intensity movements, gradually increasing duration.
- Prioritizing seated or reclined exercises to prevent sudden postural changes.
- Using compression garments to support blood circulation during workouts.
- Monitoring hydration and electrolyte balance to avoid sudden blood pressure drops.
By integrating exercise strategically, individuals with POTS can enhance daily functionality, improve long-term cardiovascular health, and minimize symptom severity with the right approach.

Best Exercise Equipment for POTS
Selecting the right exercise equipment is crucial for individuals with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS). The right tools allow for low-impact, circulation-friendly workouts that help improve vascular tone, muscle strength, and overall autonomic stability without causing excessive symptoms.
Recumbent Bikes

Recumbent bikes provide gentle cardiovascular exercise while keeping the body in a reclined position, reducing strain on circulation and preventing dizziness. Unlike upright bikes, recumbent models allow individuals to pedal while seated, ensuring better postural support and minimizing sudden heart rate fluctuations.
How to Use It Safely: Start with short cycling intervals, gradually increase resistance, and monitor hydration levels to avoid excessive fatigue.
Why It’s Beneficial: Keeps blood flowing efficiently, supports low-impact endurance building, and prevents orthostatic intolerance.
Rowing Machines
Rowing machines promote full-body engagement, strengthening the legs, core, and arms while ensuring that users remain seated throughout the workout. Since POTS patients often struggle with standing exercises, rowing provides a low-impact yet effective workout that supports circulatory function without triggering blood pooling or dizziness.
How to Use It Safely: Maintain controlled rowing speed, avoid overexertion, and take short breaks to prevent symptom flare-ups.
Why It’s Beneficial: Encourages smooth, rhythmic movement, enhances cardiovascular conditioning, and prevents excessive autonomic strain.

Resistance Bands

Using resistance bands provides a safe and controlled method for building muscle strength, reducing strain on joints and circulation. Resistance training can be done seated or reclined, making it an ideal choice for individuals who experience dizziness or low blood pressure when standing.
How to Use It Safely: Start with light resistance, focus on slow, controlled movements, and avoid excessive tension that could strain circulation.
Why It’s Beneficial: Supports progressive strength training, reduces joint stress, and helps maintain muscle tone without triggering autonomic instability.
Stability Balls
Incorporating stability balls into exercise routines improves core strength, balance, and posture, supporting healthy circulation during movement. Stability balls are particularly useful for seated workouts, allowing individuals to engage muscles without sudden positional shifts that may trigger POTS symptoms.
How to Use It Safely: Perform slow, balanced exercises, focus on posture, and maintain deep breathing to support oxygen flow.
Why It’s Beneficial: Enhances muscle endurance, encourages core stability, and supports gentle movement without excess strain.

Elevation Training Tools

For individuals experiencing blood pooling, incorporating leg elevation during exercise can help prevent symptom flare-ups. Tools such as adjustable workout benches, raised footrests, or reclining exercise chairs help maintain healthy circulation, ensuring better post-workout recovery.
How to Use It Safely: Keep legs slightly elevated, avoid prolonged inactivity, and pair elevation with gentle movement exercises to prevent circulatory stagnation.
Why It’s Beneficial: Prevents excessive blood pooling, maintains vascular efficiency, and supports postural comfort.
Treadmills
Treadmills provide controlled cardiovascular workouts, allowing individuals with POTS to adjust speed, incline, and duration based on their tolerance levels. Since walking is a moderate-intensity activity, treadmills enable gradual endurance building while minimizing sudden postural challenges.
How to Use It Safely: Start with flat incline settings, use short walking sessions, and transition from seated to standing exercises gradually to avoid dizziness or heart rate spikes.
Why It’s Beneficial: Supports controlled walking motion, promotes steady circulation, and helps progress exercise levels safely.

How to Safely Exercise with POTS
Exercising with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) requires a careful approach, prioritizing circulatory stability, gradual progression, and symptom prevention. By following structured movement techniques, individuals can build strength and endurance without triggering dizziness, fatigue, or blood pooling.
Start with Short, Low-Intensity Workouts
Exercise should begin with low-intensity, short-duration sessions, allowing the body to adjust gradually to increased activity. Overexertion can cause autonomic stress, leading to lightheadedness and excessive fatigue.
- Begin with gentle movements, such as stretching, seated cycling, or resistance band exercises, for 5–15 minutes per session.
- Gradually increase duration and resistance, ensuring the body adapts slowly without overwhelming circulation.
- Monitor heart rate and symptom responses, making adjustments based on individual tolerance levels.

Focus on Seated or Reclining Exercises
Since standing exercises can trigger dizziness and blood pooling, prioritizing seated or reclined workouts reduces strain on circulation and autonomic function.
- Recumbent bikes, rowing machines, resistance bands, and stability ball exercises provide effective movement without sudden postural shifts.
- Avoid prolonged standing exercises, focusing on controlled, seated movement patterns for maximum stability.
- If standing exercises are necessary, use compression garments and gradual positional transitions to prevent symptoms.
Use Compression Garments for Blood Flow Support
Wearing compression garments helps regulate blood circulation, preventing venous pooling in the legs and feet. Compression clothing provides vascular support, ensuring stable blood pressure during exercise.
- Use compression socks or leggings before workouts to minimize orthostatic intolerance.
- Consider abdominal binders to support core circulation, especially during longer exercise sessions.
- Ensure compression gear fits properly to avoid discomfort or restricted movement.

Stay Hydrated & Monitor Electrolyte Balance
Proper hydration and electrolyte balance are essential for POTS symptom management, preventing blood volume depletion and maintaining cardiovascular stability.
- Drink electrolyte-rich fluids before, during, and after workouts to support fluid retention.
- Monitor salt intake, ensuring adequate sodium levels to maintain blood pressure balance.
- Avoid excessive caffeine or diuretics before exercise, as they can exacerbate dehydration and fatigue.
Avoid Sudden Positional Changes
Abrupt transitions from seated to standing positions can trigger dizziness and heart rate spikes. Gradual postural shifts help prevent autonomic instability and ensure safer movement patterns.
- Transition slowly from lying to sitting, then sitting to standing, allowing circulation to adjust properly.
- Utilize supportive surfaces, such as stability bars or wall assistance, when moving between positions.
- If dizziness occurs, pause, elevate the legs
GnarlyTree | COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES
Acupuncture for POTS | How Holistic Treatments Can Support Dysautonomia Relief
Acupuncture for POTS? As patients seek alternative solutions alongside conventional care, holistic therapies like acupuncture are drawing interest for their potential to stabilize the nervous system and promote overall wellness. This post takes a deep...
FAQ | Exercise Equipment for POTS
What type of exercise equipment is best for POTS?
Recumbent bikes, rowing machines, and resistance bands are excellent choices for maintaining circulatory stability while building endurance.
Can resistance bands help strengthen muscles with POTS?
Yes, resistance bands provide controlled resistance, allowing individuals to build muscle safely without straining circulation.
Why is a recumbent bike better than an upright bike for POTS?
Recumbent bikes provide postural support, reducing blood pressure drops and dizziness compared to upright cycling.
Should individuals with POTS avoid standing exercises?
Standing exercises can increase dizziness and blood pooling, so seated and reclining workouts are generally safer.
How can stability balls help with POTS workouts?
Stability balls enhance core strength, improve balance, and support proper circulation, making them useful for gentle movement exercises.
Is elevation training beneficial for POTS symptom management?
Yes, keeping the legs slightly elevated during workouts prevents blood pooling, improving circulatory efficiency.
Can heat or compression therapy improve post-workout recovery?
Yes, compression garments and heat therapy can support muscle recovery and prevent post-exercise circulation drops.
What precautions should individuals with POTS take while exercising?
They should focus on low-impact, seated workouts, stay hydrated, and avoid sudden positional changes to maintain stability.
Does exercise worsen POTS symptoms?
If done gradually and safely, exercise strengthens circulation and reduces symptoms over time. Overexertion should be avoided to prevent flare-ups.
Should POTS patients monitor heart rate during exercise?
Yes, monitoring heart rate can help maintain safe exertion levels, ensuring that workouts remain effective without excessive strain.
Final Thoughts
Selecting the right exercise equipment is crucial for individuals with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS), ensuring that workouts remain safe, effective, and supportive of autonomic function. Since POTS affects circulation, heart rate regulation, and blood pressure stability, integrating low-impact, circulation-friendly exercises allows individuals to build strength, improve endurance, and enhance overall wellness without triggering symptoms.
By prioritizing stability, postural support, and gradual progression, individuals can reduce dizziness, fatigue, and blood pooling, making exercise a manageable and beneficial part of daily life. Choosing the right equipment ensures a customized approach to physical activity, allowing individuals with POTS to exercise confidently while maintaining symptom control.
With proper adjustments, strategic movement choices, and a focus on postural safety, exercise becomes a powerful tool for improving daily function and long-term health. A carefully tailored workout plan supports vascular efficiency, builds muscular resilience, and enhances overall well-being, making it possible to stay active while managing POTS effectively.

What is your most effective relaxation strategy for POTS?


