When managing POTS, proper diet nutrition is a vital piece of the puzzle. A well-balanced diet macronutrients for POTS can help reduce symptom severity, improve energy levels, and support autonomic stability. One key dietary principle for individuals with POTS is balancing macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each macronutrient serves a distinct function in the body, and maintaining the right proportions can support metabolic health and cardiovascular function.
This article explores how balancing macronutrients can positively impact people living with POTS and highlights practical strategies for optimizing your daily meals.
Why Macronutrient Balance Matters in POTS Management
Macronutrients influence blood sugar levels, digestion speed, and hydration—factors that directly impact POTS symptoms. For example, high-carbohydrate meals can cause postprandial hypotension (a drop in blood pressure after eating), exacerbating dizziness and fatigue in those with POTS.
Do you adjust your diet based on your POTS subtype?
Balancing carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats throughout the day can help stabilize blood sugar, maintain blood volume, and support consistent energy levels, which are crucial for managing dysautonomia.
Carbohydrates: Choose Complex, Not Simple
Carbohydrates are a necessary energy source, but not all carbs are created equal. Simple carbs like white bread, sugary drinks, and pastries are absorbed quickly, causing rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar. These fluctuations can trigger or worsen POTS symptoms.
Opt for complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index:
- Whole grains (quinoa, brown rice, oats)
- Vegetables
- Legumes
- Sweet potatoes
Pairing carbs with proteins and fats can further slow glucose absorption and reduce the likelihood of postprandial symptoms.
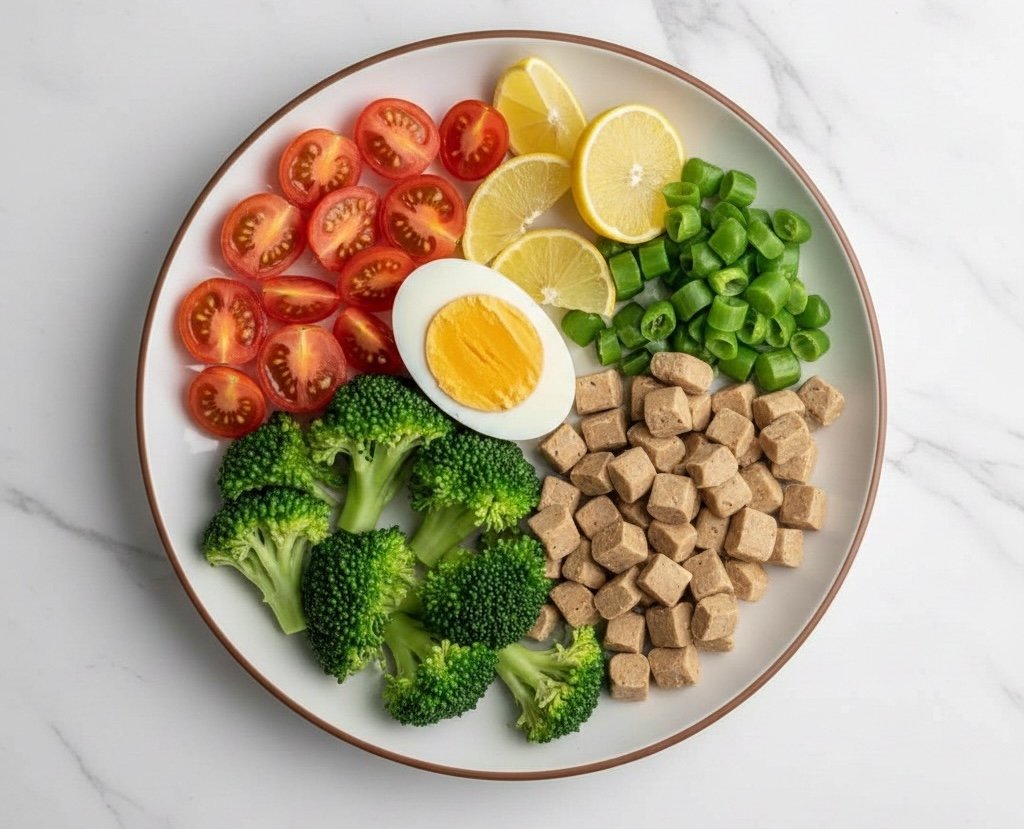
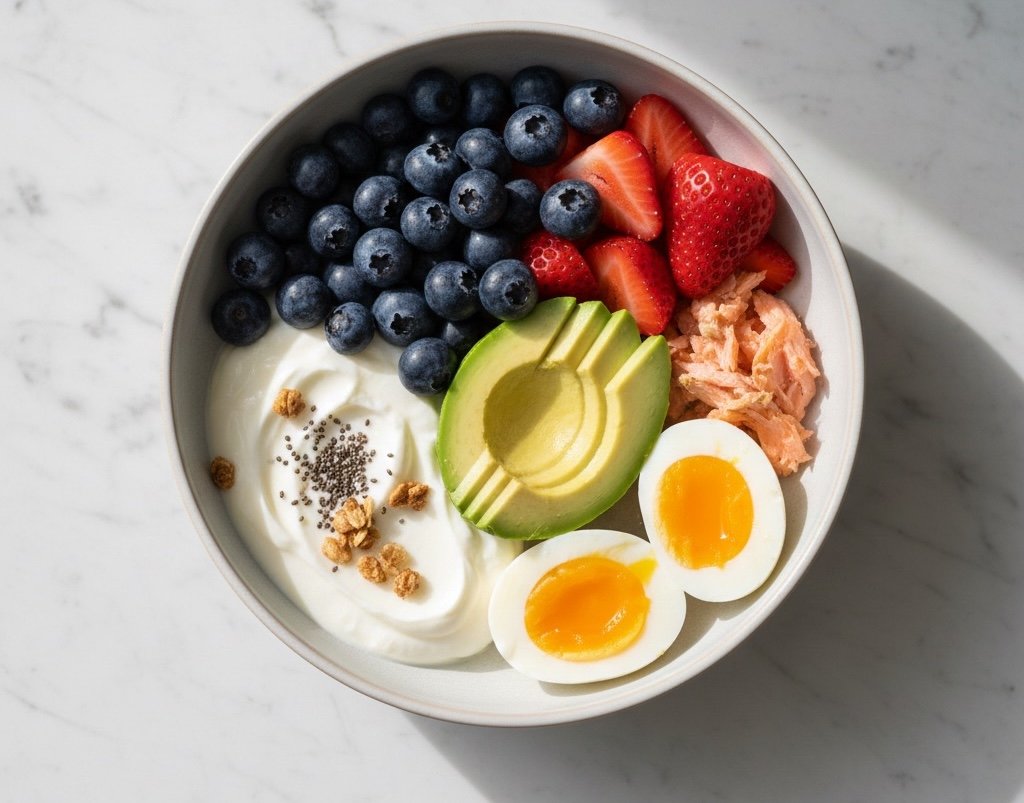

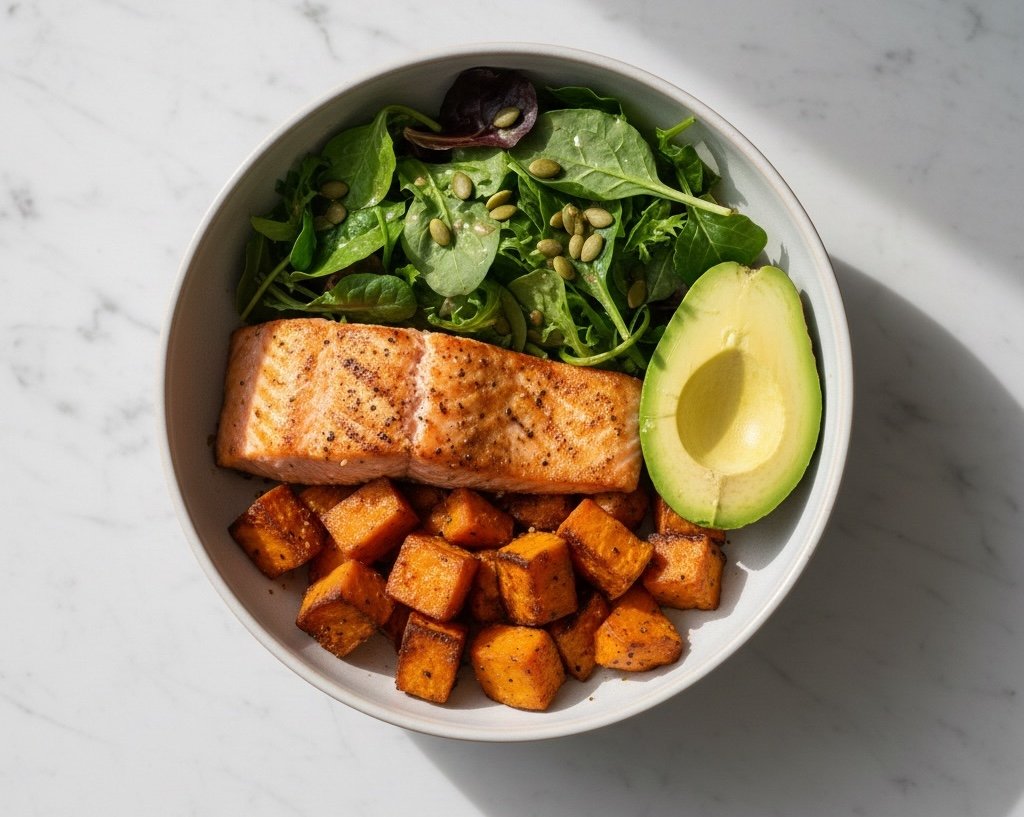

Protein: Stabilizing Blood Sugar and Supporting Muscle Function
Protein is essential for stabilizing blood sugar and supporting muscle strength, which is often reduced in POTS due to exercise intolerance. Including high-quality protein in every meal can:
- Prevent blood sugar crashes
- Promote satiety
- Support muscle recovery and blood volume maintenance
Top protein sources for people with POTS:
- Eggs
- Poultry and lean meats
- Fish and seafood
- Tofu and tempeh
- Greek yogurt
- Plant-based protein powders (for smoothies and meal supplements)
Healthy Fats: Supporting Brain Function and Energy
Fats are often overlooked, but they play a critical role in managing energy levels and inflammation. Healthy fats contribute to sustained energy release, which helps minimize crashes and fatigue in POTS patients.
Best sources of healthy fats include:
- Avocados
- Olive oil and olives
- Nuts and seeds (chia, flax, walnuts)
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Coconut oil (in moderation)
Avoid trans fats and overly processed vegetable oils, as these may contribute to inflammation and worsen symptoms.

Meal Timing and Frequency: How It Affects Macronutrient Use
In addition to macronutrient composition, when and how often you eat affects how your body handles nutrients. Many people with POTS find relief by consuming smaller, more frequent meals. This helps:
- Prevent large blood shifts to the digestive system
- Maintain steady energy
- Avoid post-meal crashes
Aim for:
- 4 to 6 smaller meals per day
- Balanced macronutrients in every meal
- Consistent timing (every 2.5–4 hours)

Sample Macronutrient-Balanced Meal Plan for POTS
Breakfast:
- Scrambled eggs with spinach and avocado
- Small serving of oatmeal with chia seeds and blueberries
Mid-Morning Snack:
- Greek yogurt with a handful of walnuts
Lunch:
- Grilled chicken quinoa bowl with roasted veggies and olive oil drizzle
Afternoon Snack:
- Apple slices with almond butter
Dinner:
- Baked salmon with sweet potato and steamed broccoli
Evening Snack (if needed):
- Cottage cheese with flaxseed and a few berries
Additional Tips for Macronutrient Balance
- Hydration: Combine a balanced diet with adequate fluid and sodium intake to support blood volume and circulation.
- Mindful eating: Eat slowly to reduce the digestive load and avoid blood pooling in the abdominal area.
- Supplements: Some individuals may benefit from electrolyte powders, B vitamins, or magnesium to support energy metabolism.
- Track symptoms: Keep a food and symptom diary to identify any intolerances or imbalances.
Collaborate with a Healthcare Provider or Dietitian
Because nutritional needs can vary significantly between individuals with POTS, it’s a good idea to work with a registered dietitian or medical provider familiar with dysautonomia. Personalized guidance can ensure you’re meeting nutritional needs without triggering symptoms.

GnarlyTree | DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & CARE
What Is The Role of a Cardiologist for POTS Patients?
Because the cardiovascular system is directly involved, cardiologists often play a central role in diagnosing, managing, and supporting patients with POTS. This post explores the critical responsibilities cardiologists have in caring for POTS patients, how...
FAQ: Macronutrients & Nutrition for POTS
1. Why is balancing macronutrients important for people with POTS?
It helps stabilize blood sugar, support blood volume, and maintain energy—reducing dizziness and fatigue.
2. What type of carbohydrates should I eat with POTS?
Choose complex carbs like whole grains, vegetables, and legumes to avoid blood sugar spikes and post-meal crashes.
3. How does protein help with POTS symptoms?
Protein stabilizes blood sugar, supports muscle strength, and helps maintain blood volume, all of which can improve symptoms.
4. What are the best sources of protein for POTS?
Eggs, lean meats, fish, tofu, Greek yogurt, and plant-based protein powders are all excellent options.
5. Why are healthy fats important in a POTS-friendly diet?
They provide steady energy, reduce inflammation, and support brain function without causing blood sugar crashes.
6. How often should someone with POTS eat?
Eating every 2.5 to 4 hours in smaller, balanced meals helps prevent drops in blood pressure and energy crashes.
7. What should a balanced POTS-friendly meal include?
Each meal should have complex carbs, lean protein, healthy fats, and a hydrating component like fruits or vegetables.
8. Should I track what I eat with POTS?
Yes, keeping a food and symptom diary can help identify helpful foods and avoid triggers more effectively.
Conclusion
Balancing macronutrients is a simple but powerful tool in managing POTS symptoms. By prioritizing complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats, individuals with POTS can promote better blood sugar regulation, increase energy stability, and reduce the risk of postprandial hypotension.
Incorporating these principles into a daily routine—along with proper hydration, meal timing, and medical support—can significantly improve quality of life for those living with this form of dysautonomia.
What is your most effective relaxation strategy for POTS?


