Medical Equipment is Vital for POTS Management
Managing POTS requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medical support, and specialized Medical Equipment for POTS to ease symptoms and improve daily functionality. The right medical tools can aid circulation, heart rate regulation, hydration balance, and mobility, making life with POTS more manageable. Whether you’re looking for compression gear, monitoring devices, or hydration solutions, selecting the right equipment tailored to your specific needs can enhance symptom control and promote overall well-being.
POTS affects the autonomic nervous system, making it difficult for the body to regulate blood pressure, heart rate, and circulation. Many individuals experience symptoms like dizziness, tachycardia, blood pooling, fatigue, and temperature dysregulation, which can significantly interfere with daily activities.
Using medical equipment designed for autonomic dysfunction can help stabilize key body functions, prevent symptom flare-ups, and offer continuous monitoring for better long-term management.
What is your biggest challenge with exercising?
Compression Garments
How Compression Supports Circulation
Compression garments are a vital tool for managing POTS symptoms, as they help maintain blood circulation and prevent excessive venous pooling in the lower extremities. By applying gentle pressure to the legs, abdomen, or full body, these garments encourage proper blood flow, allowing more oxygenated blood to reach the brain and reducing lightheadedness and dizziness upon standing.
Types of Compression Garments for POTS
Compression Socks
Graduated compression socks improve venous return, reducing blood pooling in the legs. They come in varying pressure levels, with 20-30 mmHg being a common recommendation for POTS patients.
Compression Leggings
These provide full-leg support, helping regulate circulation across the lower extremities while offering increased mobility and comfort compared to socks alone.
Abdominal Binders
Since blood pooling can also affect the abdomen, compression binders offer added support, improving blood pressure stability and reducing symptoms such as fatigue and orthostatic intolerance.
Choosing the Right Compression Level
Selecting the appropriate compression intensity is essential for maximizing benefits without discomfort. Common pressure ranges include:
- Mild compression (10-20 mmHg) – Suitable for general circulation support.
- Moderate compression (20-30 mmHg) – Recommended for individuals experiencing significant blood pooling and orthostatic symptoms.
- Firm compression (30-40 mmHg) – Used in cases of severe dysautonomia, often prescribed by medical professionals.
Integrating Compression Garments Into Daily Life
To optimize symptom relief:
- Wear compression garments in the morning before standing for prolonged periods.
- Pair compression wear with hydration and electrolyte strategies for enhanced blood volume regulation.
- Experiment with different garment types and pressure levels to determine the most effective combination for personal comfort and symptom control.
Using compression garments strategically can provide daily stability, preventing dizziness and improving overall vascular function in POTS management.
This section now follows proper Gutenberg-friendly formatting, ensuring clarity and logical structure. Let me know if you’d like refinements or if we’re ready to expand another section!

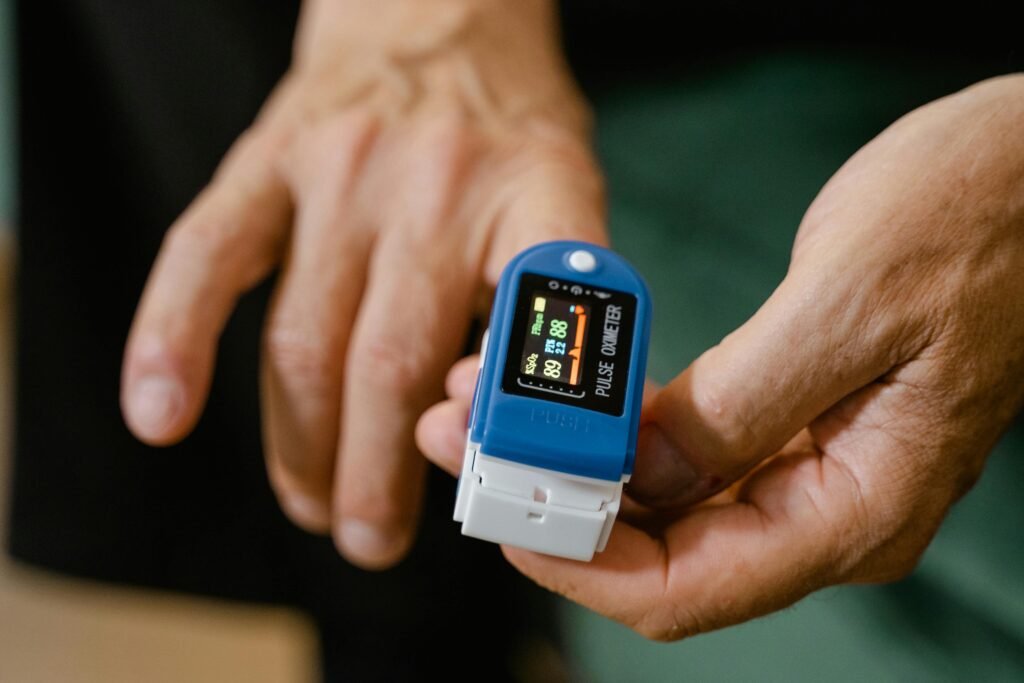
Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Monitors
The Importance of Monitoring for POTS
POTS causes fluctuations in heart rate and blood pressure, often leading to lightheadedness, tachycardia, and blood pooling. Using digital monitors allows individuals to track these variations in real time, helping them adjust daily activity levels and providing valuable data for doctors overseeing treatment plans. Regular monitoring can reveal patterns, identify triggers, and guide preventative strategies to minimize symptom flare-ups.
Choosing the Right Monitoring Device
Digital Blood Pressure Monitors
Traditional upper-arm cuff monitors remain the most reliable option for tracking blood pressure changes. They offer precise readings, which are critical for managing symptoms like low blood volume and blood pressure instability. Wrist-based monitors can be convenient but tend to be less accurate, especially for autonomic dysfunction patients.
Heart Rate Monitors
Devices such as chest strap monitors or wearable pulse trackers help assess tachycardia episodes and detect sudden heart rate spikes when transitioning from sitting to standing. High-frequency monitoring ensures more accurate trends, which can support better treatment adjustments.
Smartwatches for Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Monitoring
Smartwatches now integrate heart rate tracking and blood pressure monitoring, making them convenient tools for symptom management on the go. These devices use optical sensors (PPG technology) to track heart rate, while some advanced models offer ECG features for more precise cardiovascular assessments.
Limitations of Smartwatch-Based Monitoring
While heart rate tracking in smartwatches is generally reliable, blood pressure monitoring often requires manual calibration using a traditional cuff to improve accuracy. Only select models provide FDA-approved blood pressure tracking, ensuring more dependable results.
Using Monitors for Symptom Management
To optimize tracking:
- Record baseline readings in the morning and throughout the day to observe fluctuations.
- Set alerts for abnormal readings, helping manage sudden drops or spikes.
- Use tracking alongside lifestyle adjustments such as hydration strategies, physical therapy, and medication guidance.
While smartwatches and digital monitors enhance convenience, they should complement—rather than replace—traditional medical devices for comprehensive symptom management. Combining multiple tracking methods ensures the most accurate assessment and effective care for POTS patients.
Electrolyte Solutions and IV Hydration Support
The Role of Hydration in POTS Management
For individuals with POTS, low blood volume contributes to symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and brain fog. Proper hydration enhances circulatory stability, helping to maintain blood pressure and reduce orthostatic intolerance. Increasing fluid intake supports vascular function, ensuring that oxygenated blood reaches the brain more effectively upon standing.
Electrolyte Solutions for Daily Hydration
Balanced Electrolyte Drinks
Electrolyte-rich beverages replenish sodium, potassium, and magnesium, preventing dehydration and improving blood volume retention. Common options include:
- Oral rehydration solutions (ORS) designed for medical-grade hydration.
- Sports drinks with added electrolytes—but watch for excess sugar content.
- Electrolyte powders mixed with water for customizable hydration.
- Homemade electrolyte solutions, including a mixture of water, salt, lemon, and honey.
Sodium Intake for Improved Circulation
Since sodium boosts fluid retention, many POTS patients benefit from higher daily sodium intake. Adding salted snacks or incorporating salt capsules alongside electrolyte drinks enhances hydration efficiency.
IV Hydration Therapy for Severe Cases
When is IV Hydration Necessary?
While daily fluid intake helps manage mild to moderate symptoms, some individuals experience persistent dizziness, weakness, or tachycardia despite adequate hydration. In such cases, intravenous (IV) fluids provide rapid symptom relief by delivering saline and electrolytes directly into the bloodstream.
Types of IV Hydration Solutions
- Normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride) – A widely used IV fluid for stabilizing blood volume.
- Lactated Ringer’s solution – Contains additional potassium and calcium, beneficial for electrolyte balance.
- Customized IV treatments – Some clinics offer infusions with magnesium or B vitamins, tailored to individual needs.
Integrating Hydration into Daily Management
To maximize benefits:
- Maintain consistent fluid intake throughout the day, rather than consuming large amounts at once.
- Pair hydration strategies with compression garments for better circulation.
- Discuss IV therapy options with a specialist if symptoms remain severe despite proper electrolyte balance.

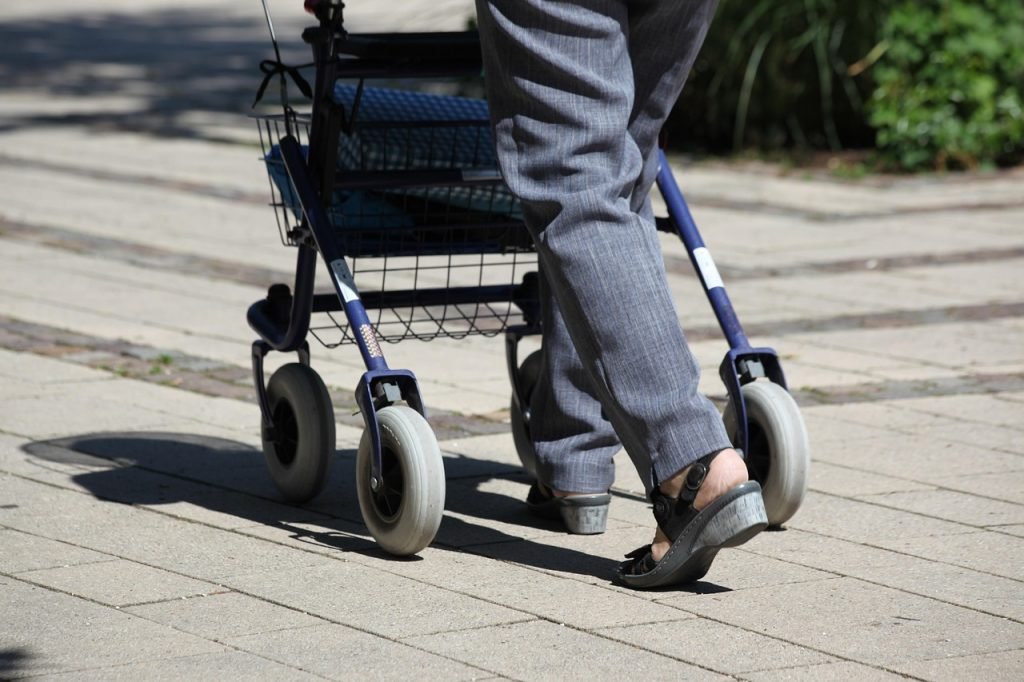
Mobility Aids
How Mobility Aids Support POTS Management
Severe dizziness, fatigue, and muscle weakness can make standing or walking difficult for individuals with POTS. Mobility aids provide crucial stability and fall prevention, enabling safer movement and greater independence while managing symptoms. Choosing the right device depends on symptom severity, daily activity levels, and specific mobility challenges.
Types of Mobility Aids for POTS
Canes for Mild Stability Support
- Ideal for mild balance issues and occasional dizziness.
- Single-point canes offer lightweight support, while quad canes provide extra stability for unsteady movement.
- Adjustable height options accommodate individual posture needs.
Walkers for Greater Balance Assistance
- Standard walkers provide full-body support, reducing strain on muscles during movement.
- Rollator walkers with wheels enhance mobility for those who need stability but also want smoother movement.
- Some models include built-in seating, allowing users to rest when symptoms become overwhelming.
Wheelchairs for Severe Mobility Impairment
- Used when standing or walking triggers extreme symptoms such as fainting or severe tachycardia.
- Manual wheelchairs allow self-propelled movement, while power wheelchairs offer adjustable positioning for customized support.
- Lightweight transport chairs help navigate public spaces easily without excessive strain.
Integrating Mobility Aids Into Daily Life
To make mobility aids more effective:
- Choose a device suited to symptom severity, ensuring comfort and maneuverability.
- Pair mobility aids with compression garments and hydration strategies for better circulation.
- Practice gradual movement adjustments, using aids to prevent sudden postural shifts.
Using mobility aids strategically empowers individuals with POTS to maintain independence, minimize falls, and navigate daily life with greater ease.

Cooling and Heating Devices
Managing Temperature Dysregulation in POTS
Individuals with POTS often experience difficulty regulating body temperature, leading to heat intolerance, excessive sweating, or sudden chills. Using cooling and heating devices helps maintain a comfortable temperature, reducing symptom severity and preventing additional stress on the autonomic nervous system.
Cooling Devices for Heat Sensitivity
Cooling Vests
- Provide continuous cooling by using gel packs or evaporative technology.
- Ideal for hot climates or prolonged outdoor activities.
- Lightweight designs ensure comfort without restricting movement.
Portable Fans and Cooling Towels
- Battery-operated fans help circulate air, preventing overheating.
- Cooling towels, activated with water, rapidly lower skin temperature.
Moisture-Wicking Fabrics
- Reduce sweat accumulation by promoting breathability.
- Help regulate body temperature, keeping skin dry and cool.
Heating Devices for Cold Sensitivity
Heated Blankets and Pads
- Deliver consistent warmth to reduce cold-induced muscle tension.
- Adjustable temperature settings ensure controlled comfort.
Hand Warmers and Heated Clothing
- Rechargeable heated gloves and socks keep extremities warm.
- Wearable heat packs provide on-demand warmth during outdoor activities.
Incorporating Temperature Regulation into Daily Life
To optimize comfort and symptom management:
- Adjust clothing layers based on environmental conditions.
- Use temperature-modifying devices strategically during symptom-prone periods.
- Pair cooling and heating tools with hydration strategies for better autonomic balance.
Maintaining stable body temperature with these supportive tools helps individuals with POTS minimize temperature-related flare-ups, ensuring greater daily comfort and symptom control.

Adjustable Beds and Wedge Pillows
How Elevation Supports POTS Management
Sleeping with a slightly elevated upper body helps mitigate morning dizziness, improve blood circulation, and prevent fluid pooling in the legs overnight. By maintaining an optimal sleep position, individuals with POTS can experience fewer orthostatic symptoms upon waking, leading to improved daily functionality and reduced fatigue.
Benefits of Adjustable Beds
Customizable Elevation Settings
Adjustable beds allow users to fine-tune their sleep position, offering precise control over upper-body incline to prevent overnight blood pooling.
Improved Circulatory Flow
Keeping the head and torso elevated promotes venous return, helping oxygenated blood reach the brain more effectively.
Enhanced Comfort for Symptom Relief
Adjustable beds often come with memory foam or orthopedic mattresses, reducing pressure points and supporting proper spinal alignment.
Wedge Pillows as a Practical Alternative
Affordable and Portable
Wedge pillows provide gradual elevation without requiring a full bed adjustment, making them a cost-effective and versatile option.
Positioning Versatility
They can be used under the upper body, beneath the legs, or in combination to support individual sleep needs.
Maintaining Blood Pressure Stability
Elevated positioning reduces the risk of morning hypotension, ensuring smoother transitions from lying down to standing.
Optimizing Sleep for POTS Management
To maximize benefits:
- Adjust incline gradually to find the most effective elevation level.
- Pair elevated sleep positions with hydration strategies to improve circulatory stability.
- Use compression garments in the morning to reinforce overnight vascular support.
Maintaining a strategic sleep posture with adjustable beds or wedge pillows can significantly improve POTS symptom regulation, making mornings more manageable and reducing daily discomfort.

How to Choose the Right Equipment for Your Needs
Assessing Symptom Severity
Each individual with POTS experiences symptoms differently, making personalized equipment selection essential. Consider which symptoms impact daily life the most—whether it’s frequent dizziness, circulation issues, fatigue, or mobility challenges.
- If blood pooling and orthostatic intolerance are primary concerns, compression garments may be most beneficial.
- If tachycardia and blood pressure fluctuations require constant monitoring, heart rate and blood pressure monitors should be prioritized.
- For severe mobility impairments, choosing canes, walkers, or wheelchairs can provide necessary support.
Lifestyle Compatibility
Medical equipment should seamlessly integrate into daily routines without creating unnecessary inconvenience.
- Portable heart monitors or smartwatches allow discreet tracking throughout the day.
- Lightweight compression wear ensures easy movement while offering circulatory benefits.
- Compact hydration solutions, such as electrolyte packets, fit effortlessly into daily routines.
Consulting Medical Professionals
Before incorporating new devices into symptom management, consult with healthcare providers. They can:
- Recommend equipment based on individual health assessments.
- Adjust treatment plans based on monitored data trends.
- Ensure proper usage of medical tools for maximum effectiveness.
Balancing Multiple Tools for Comprehensive Management
Since POTS affects multiple body systems, combining different tools may provide more effective symptom relief. Using hydration strategies, mobility aids, compression therapy, and monitoring devices together enhances overall stability and comfort.
By choosing symptom-targeted, lifestyle-compatible, and professionally recommended equipment, individuals with POTS can better navigate daily life with greater independence and symptom control.

GnarlyTree | NON-MEDICAL EQUIPMENT
POTS Symptoms Tracking Apps | Choosing the Best Tools for Monitoring Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
What Makes a Great POTS Tracking App? POTS Symptoms Tracking Apps have evolved to deliver highly personalized, data-driven support for individuals managing postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. These tools help users track key metrics, identify symptom...
FAQ Section
What is the most important medical equipment for managing POTS?
Compression garments, heart rate monitors, and hydration aids are among the most essential tools for symptom control.
Can compression socks really help with POTS symptoms?
Yes, they improve circulation, reduce blood pooling, and support blood pressure regulation, making standing easier.
Should I track my heart rate daily with POTS?
Monitoring heart rate and blood pressure regularly helps identify symptom patterns and guide treatment adjustments.
How does hydration impact POTS management?
Proper hydration supports blood volume, preventing dizziness, fainting, and fatigue associated with POTS.
Are mobility aids necessary for POTS patients?
For individuals experiencing severe dizziness or weakness, mobility tools like canes or wheelchairs provide stability and safety.
What type of bed is best for someone with POTS?
Adjustable beds or wedge pillows allow for upper body elevation, improving circulation and reducing morning symptoms.
Do cooling vests help with POTS temperature regulation?
Yes, cooling vests prevent overheating, helping individuals manage autonomic temperature fluctuations more effectively.
Should I consult a doctor before using new medical equipment?
Absolutely! A doctor’s guidance ensures proper integration of medical devices into your treatment and lifestyle.
Can IV hydration help with POTS symptoms?
For severe cases, IV hydration can quickly restore fluids and reduce dizziness, especially in individuals with chronic dehydration issues.
Is medical equipment covered by insurance for POTS patients?
Coverage varies, but some mobility aids, monitors, and compression garments may be eligible for reimbursement or insurance support.
Final Thoughts
Effectively managing POTS symptoms requires a multifaceted approach that integrates strategic medical equipment, continuous symptom tracking, and hydration support. By utilizing compression therapy, mobility aids, and real-time monitoring, individuals can significantly improve daily functionality and overall well-being.
Selecting the right tools based on symptom severity, lifestyle compatibility, and professional recommendations ensures a personalized symptom management plan. Thoughtfully incorporating these strategies helps reduce discomfort, enhance circulation, and promote autonomic stability for long-term relief. Consulting healthcare providers for guidance and adjustments ensures the most effective and sustainable symptom management approach tailored to individual needs.
Do you have a secondary condition that causes your POTS?