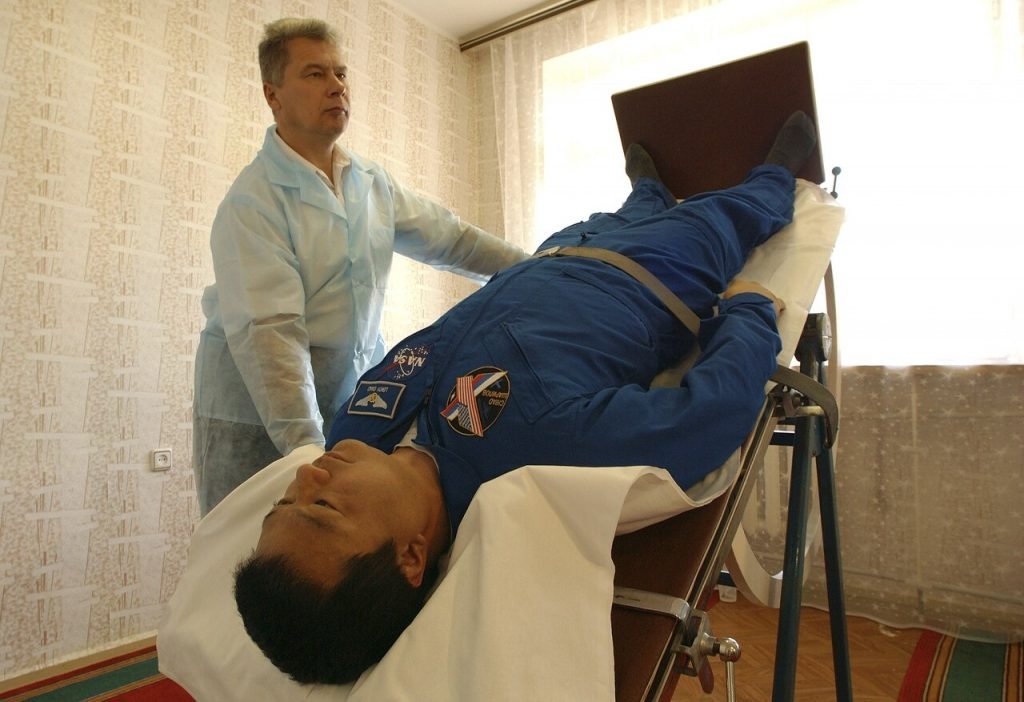
Understanding the Nervous System and Sudomotor Function
The Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test (QSART) is a specialized diagnostic tool used to assess the small nerve fibers that control sweating. These fibers, part of the autonomic nervous system, are essential for regulating body temperature and maintaining proper skin hydration. When they malfunction, the result may point to autonomic neuropathy or other nerve-related conditions—often early indicators of systemic disorders such as diabetes, multiple system atrophy, or autoimmune disease.
Whether you’re navigating troubling symptoms or under evaluation for a neurological condition, understanding QSART empowers patients and caregivers with clarity about what the test shows and how to interpret the results.
The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary body functions—including heart rate, digestion, blood pressure, and sweating. Within this system, sudomotor nerves specifically control the sweat glands. Any breakdown in these small nerve fibers can alter how your body responds to temperature changes or stress. That’s where QSART becomes particularly valuable—it precisely measures sweat output at targeted sites in response to a small electrical stimulus.
Have you found water-based exercises to be helpful?
The test evaluates the integrity of postganglionic sympathetic fibers—the specific nerves affected in various small fiber neuropathies. It’s often conducted alongside other autonomic tests, such as tilt table testing or heart rate variability, to form a more complete diagnostic picture.
How QSART Works: A Step-by-Step Overview
- Preparation: You’ll typically rest in a temperature-controlled room to ensure consistent baseline readings. Avoid lotions or moisturizers beforehand, as these can affect the skin’s conductivity.
- Electrode Placement: Four small sweat capsules—attached to electrodes—are placed on specific skin areas, usually the forearm, foot, leg, and upper chest.
- Acetylcholine Delivery: A mild electrical current delivers acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter, into the skin. This simulates the body’s natural nerve signals that trigger sweat production.
- Response Monitoring: Sensors measure the amount and timing of sweat produced at each site. Delays or absence of sweating in specific regions may indicate small fiber nerve dysfunction.
- Duration: The process takes around 45 minutes, is non-invasive, and causes minimal discomfort—usually described as a tingling or warming sensation.

Why QSART Is Used in Clinical Settings
QSART plays a crucial role in diagnosing and tracking the progression of autonomic neuropathies. It’s frequently ordered when patients report symptoms like:
- Unexplained dry skin or excessive sweating
- Dizziness on standing (orthostatic hypotension)
- Abnormal skin flushing or temperature intolerance
- Burning, tingling, or numbness in the hands or feet
Conditions that benefit from QSART testing include diabetic neuropathy, POTS (postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome), small fiber neuropathy, autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy, multiple system atrophy, and amyloidosis.
By isolating where the nerve breakdown occurs, QSART can differentiate between pre- and postganglionic lesions, informing treatment strategies and guiding neurologists toward more focused testing.
Benefits of QSART Compared to Other Neuropathy Tests
Unlike other autonomic tests that rely on systemic stressors like deep breathing or standing (e.g., tilt table test), QSART isolates nerve pathways locally—allowing for highly specific analysis. This precision makes it valuable for:
- Detecting early changes in small fiber function
- Monitoring disease progression over time
- Comparing sweat response across different body regions
- Ruling out central nervous system involvement when results are normal
Because it targets peripheral nerve endings, QSART can reveal dysfunction even when traditional nerve conduction studies appear normal—making it a preferred method when small fiber involvement is suspected.
How to Prepare for a QSART Exam
To get the most accurate results, proper test preparation is important. Your physician may advise:
- Avoiding caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol for 24 hours before the test
- Not using lotions or skin products on the testing day
- Wearing loose, comfortable clothing
- Informing your doctor of any medications, as some can affect sweat response
It’s also worth noting that anxiety and stress can impact results, so staying relaxed in the testing environment helps ensure accuracy.
What QSART Results Mean
Results are evaluated based on the amount and latency of sweat response from each electrode site. Reduced or absent response may suggest length-dependent neuropathy, especially if the lower extremities are affected more than the upper. In contrast, patchy or localized abnormalities may indicate focal nerve damage or autoimmune conditions.
Interpretation must be made in context with other test results, symptoms, and medical history. While QSART can’t confirm a specific diagnosis on its own, it adds valuable insight into the functional status of autonomic nerves.

GnarlyTree | DIAGNOSTIC TESTS & CARE
What is the Role of a Physical Therapist for POTS
Living with POTS can be overwhelming, but physical therapy plays a vital role in helping patients regain strength, improve circulation, and manage symptoms effectively. This article explores how physical therapists support individuals with POTS, offering...
Frequently Asked Questions
What does the QSART test actually measure?
It measures sweat production in response to controlled stimulation, indicating the health of small autonomic nerve fibers.
Is QSART painful or invasive?
No, QSART is non-invasive and generally well tolerated. Most people feel only mild tingling or warmth.
How long does a QSART test take?
The entire procedure typically takes 45 minutes to an hour, including setup and monitoring.
Can I eat or drink before the test?
Yes, but avoid stimulants like caffeine or nicotine for at least 24 hours prior for accurate results.
What conditions is QSART commonly used to diagnose?
QSART helps diagnose small fiber neuropathy, autonomic dysfunction, diabetic neuropathy, and other disorders affecting sweat regulation.
Will I get my results immediately?
Not always. Your neurologist will interpret results alongside other tests, and may need time to assess the full picture.
Can medications affect QSART results?
Yes, certain medications—especially those affecting the nervous system—can impact sweat response. Always inform your physician beforehand.
Is QSART covered by insurance?
Often yes, especially if part of an autonomic or neuropathy workup. Check with your provider for specifics.
How accurate is QSART in diagnosing neuropathy?
It’s highly sensitive for detecting small fiber nerve dysfunction and can catch issues that standard nerve tests may miss.
Are there alternatives to QSART?
Yes, other tests include thermoregulatory sweat testing (TST), skin biopsy, and autonomic reflex screens, depending on your symptoms and medical context.
Final Thoughts
The QSART (Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test) is a powerful, targeted tool for evaluating the function of small autonomic nerve fibers. Especially useful in cases of unexplained symptoms or suspected small fiber neuropathy, it adds a layer of clarity that guides diagnosis and future treatment. While no single test tells the whole story, QSART brings precision and nuance to the complex world of autonomic diagnostics—empowering both patients and clinicians with meaningful, actionable insight.
Do you pre-hydrate with electrolytes before exercising?