Understanding the Need for Testing
Why Testing is Essential for POTS Diagnosis
POTS Tests are vital for understanding. POTS is often misdiagnosed or overlooked due to the complexity and variability of its symptoms. Many individuals struggle for years before receiving an accurate diagnosis, as symptoms can mimic other conditions like chronic fatigue syndrome, anxiety disorders, or cardiovascular issues. Autonomic function tests provide objective measurements that differentiate POTS from other conditions, ensuring proper treatment and symptom management.
Common Challenges in Diagnosis
Since POTS presents with diverse symptoms, doctors may initially attribute dizziness, fatigue, or heart palpitations to dehydration, anxiety, or even inner-ear disorders. Standard blood pressure and heart rate checks during routine examinations often fail to detect autonomic dysfunction, making specialized testing crucial. Additionally, symptom severity can fluctuate, leading to inconsistent results if assessments are not conducted properly or under controlled conditions.
Who Should Consider Testing?
Individuals experiencing persistent symptoms, such as lightheadedness upon standing, excessive fatigue, brain fog, and heart rate fluctuations, should consider autonomic function assessments. Those with underlying conditions like Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, autoimmune disorders, or post-viral syndromes may have a higher risk of developing POTS, making early testing even more vital.
Do you have a comorbid condition with your POTS?
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Identifying POTS early allows for more effective symptom management and prevents further complications. Without proper diagnosis, individuals may struggle with daily activities, reduced physical endurance, and unpredictable symptom flares. By undergoing autonomic function testing, patients can gain clarity on their condition and receive targeted treatment plans that improve overall quality of life.
Key Autonomic Function Tests for POTS
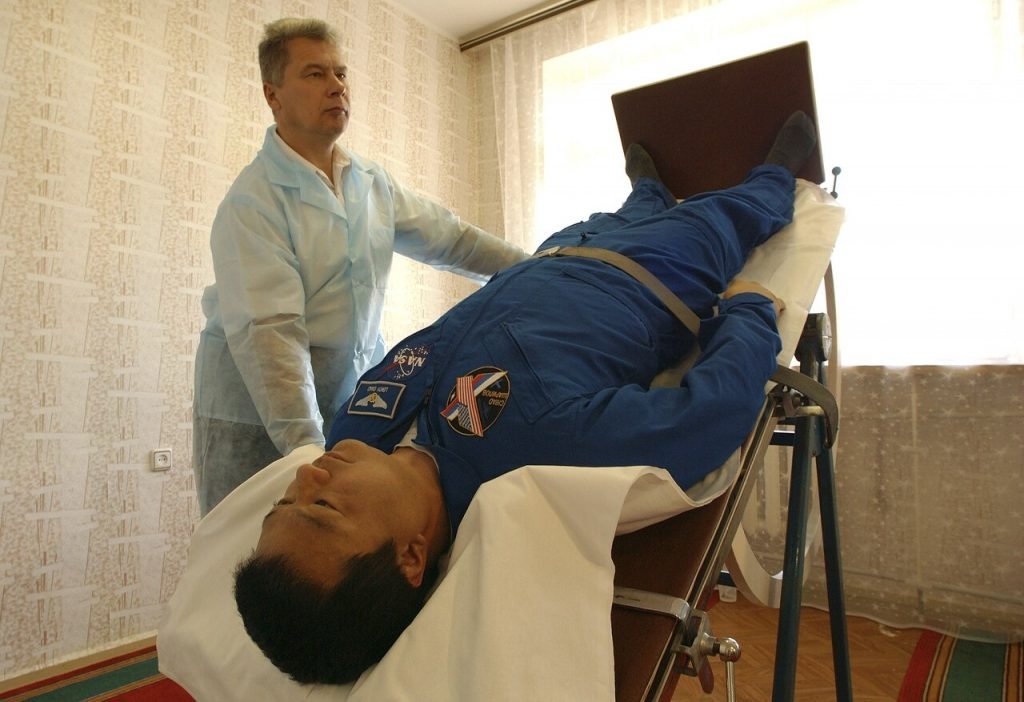
Tilt Table Test
The tilt table test is a gold-standard assessment for POTS. The patient is strapped to a motorized table that gradually moves from lying to a near-standing position while heart rate and blood pressure are monitored. Individuals with POTS typically experience an abnormal heart rate increase upon standing, confirming autonomic dysfunction.
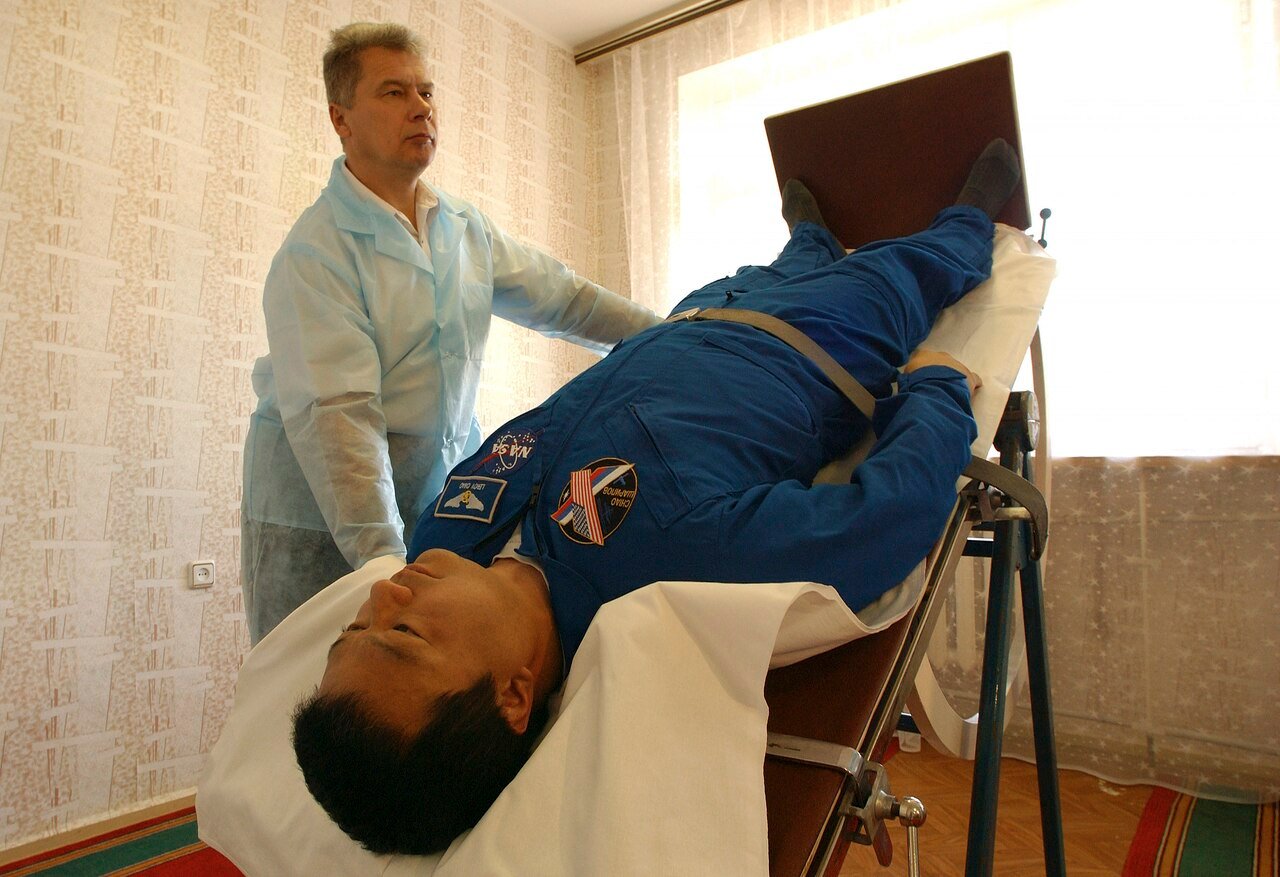
Active Stand Test
This test serves as a simplified alternative to the tilt table test. The patient transitions from lying down to standing upright while medical professionals track changes in heart rate and blood pressure. A persistent increase in heart rate of more than 30 beats per minute (or 40 bpm for those under 19) indicates POTS.

QSART (Quantitative Sudomotor Axon Reflex Test)
This test evaluates the autonomic nerves controlling sweat production. Electrodes stimulate the skin, and the sweat response is measured. Abnormal results may indicate autonomic dysfunction linked to POTS.
Autonomic Blood Pressure Monitoring
This involves continuous blood pressure measurement while performing different postural changes. It helps determine if patients experience abnormal fluctuations, contributing to dizziness and syncope.
Valsalva Maneuver
This assessment examines the autonomic nervous system’s response to forceful breathing against a closed airway. Variations in heart rate and blood pressure provide insight into autonomic function and may indicate POTS-related dysregulation.
Heart Rate Variability Testing
This method tracks how the heart rate adapts to stress, breathing patterns, and positional shifts, offering a deeper understanding of autonomic control mechanisms in POTS patients.

Preparing for POTS Testing
Dietary and Medication Considerations
Before autonomic function testing, certain substances can interfere with results, potentially masking or exaggerating autonomic dysfunction. It’s recommended to avoid caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine for at least 24 hours before the test, as these can affect heart rate and circulation. Some medications, including beta-blockers, antihistamines, and certain antidepressants, may alter autonomic responses, so patients should consult their doctor about whether temporary adjustments are necessary.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Proper hydration is crucial to stabilizing blood pressure and preventing unnecessary symptom exacerbation during testing. Increasing fluid intake, especially electrolyte-rich drinks, ensures optimal blood volume and reduces dizziness. Consuming sodium-rich foods, such as salted nuts or electrolyte supplements, may help maintain vascular stability. However, excessive fluid intake immediately before testing might lead to artificially favorable results, so moderation is key.

Clothing and Physical Comfort
Wearing loose, comfortable clothing can help minimize discomfort, especially during prolonged testing sessions. Many assessments require periods of standing or lying down, so dressing in layers allows for temperature regulation. Compression garments, such as compression socks, should generally be avoided before testing, as they may influence circulatory measurements.
Support and Safety Measures
Some autonomic tests may trigger dizziness, nausea, or temporary weakness. Bringing a friend or family member for support ensures help is available if symptoms become overwhelming. If testing is conducted at a specialized autonomic clinic, staff are equipped to handle adverse reactions, but personal support can provide an additional level of reassurance.
Mental and Physical Preparation
Testing may require extended periods of lying still or standing upright, which can be challenging for POTS patients. Practicing deep breathing techniques and engaging in gentle stretching beforehand can improve tolerance. Additionally, scheduling tests earlier in the day when energy levels are more stable may enhance accuracy.
Understanding Test Results
Interpreting Autonomic Function Data
Once autonomic function tests are completed, doctors analyze the collected data to determine how well the nervous system regulates heart rate, blood pressure, and circulation. A heart rate increase of more than 30 beats per minute (or 40 bpm for individuals under 19) upon standing is a key diagnostic marker for POTS. Additional test results may indicate autonomic dysfunction, such as abnormal blood pressure fluctuations, impaired sweating responses, or irregular heart rate variability.
Confirming a POTS Diagnosis
A definitive POTS diagnosis relies on both test results and symptom history. Doctors look for patterns of chronic symptoms that align with autonomic dysfunction, including dizziness, brain fog, heart palpitations, and exercise intolerance. Since test results can vary based on hydration levels, medications, and time of day, multiple assessments may be required for accuracy.
Developing a Management Plan
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, treatment focuses on improving circulation, minimizing symptoms, and enhancing overall quality of life. Key components of a personalized POTS management plan often include:
- Hydration strategies to support blood volume and prevent dizziness
- Electrolyte and sodium intake adjustments to stabilize blood pressure
- Medications, such as beta-blockers or vasopressors, to regulate autonomic function
- Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises to strengthen cardiovascular endurance
- Dietary modifications, avoiding excessive sugar and processed foods that worsen symptoms
Next Steps After Diagnosis
Patients may need follow-up autonomic assessments to monitor changes in function over time. Working closely with specialists—such as cardiologists, neurologists, or physical therapists—ensures a tailored approach to symptom control. Understanding test results allows individuals to advocate for effective treatment strategies and make informed lifestyle adjustments to manage POTS more effectively.

GnarlyTree | TYPES OF POTS
What is Dysautonomia? | Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
What is Dysautonomia? The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for regulating many of the body’s automatic functions—things we often take for granted, like maintaining a steady heart rate, digesting food efficiently, and keeping blood...
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most accurate test for diagnosing POTS?
The tilt table test is considered the most definitive diagnostic tool, as it provides controlled conditions to observe autonomic dysfunction and abnormal heart rate response.
Can POTS tests be done at home?
While informal active stand tests can be attempted at home, proper diagnosis requires medical-grade autonomic assessments performed by specialists.
Do I need multiple tests to confirm POTS?
Yes, doctors typically use a combination of tests to rule out other conditions and assess various autonomic functions before confirming a POTS diagnosis.
How long does POTS testing take?
Depending on the specific assessments performed, testing can range from 30 minutes to a few hours. Some tests require follow-up evaluations for accurate results.
What should I do if my autonomic test results are inconclusive?
If results are unclear, consulting a specialist for further testing and symptom tracking can provide a more precise diagnosis.
Final Thoughts
POTS testing plays a vital role in uncovering autonomic dysfunction and tailoring effective treatment strategies. By undergoing comprehensive assessments, individuals gain clarity on their condition, allowing for informed decisions on symptom management. Early diagnosis leads to better lifestyle adaptations, ensuring long-term stability and improved daily function. With the right approach, patients can work toward enhanced quality of life, navigating POTS with confidence and control.
Have you found L-carnitine helpful for your POTS?