Hypovolemic POTS is a distinct subtype of POTS and falls within the broader group of autonomic nervous system disorders known as dysautonomia. This form of POTS is primarily characterized by a reduced blood volume (hypovolemia), which affects the body’s ability to maintain proper blood flow when upright, leading to a cascade of symptoms that can severely affect daily functioning.
Understanding hypovolemic POTS is crucial for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals in order to develop tailored strategies for diagnosis and management. In this post, we will explore the nature of hypovolemic POTS, its symptoms, causes, diagnostic criteria, and treatment approaches.
Defining Hypovolemic POTS
Hypovolemic POTS is characterized by a reduced circulating blood volume, which results in inadequate blood return to the heart when standing. This deficiency causes the heart to pump faster to compensate for reduced perfusion, leading to symptoms associated with orthostatic intolerance.
What is your experience with juicing for POTS?
Common Symptoms of Hypovolemic POTS
- Rapid heart rate upon standing
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Nausea
- Brain fog
- Exercise intolerance
- Cold extremities
- Palpitations
- Shakiness
- Low blood pressure (in some cases)
These symptoms often worsen with prolonged standing, heat exposure, dehydration, or after meals. They may overlap with other types of POTS, making a precise diagnosis important.
Causes and Risk Factors
The underlying cause of hypovolemic POTS is not always clear, but several contributing factors are recognized:
- Low plasma and red blood cell volume: Inadequate circulating volume reduces venous return and cardiac output.
- Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) dysfunction: This hormonal system helps regulate blood volume and pressure, and may be impaired in POTS patients.
- Dehydration: Chronic or recurrent dehydration can exacerbate blood volume deficiencies.
- Genetics and familial trends: Some patients have a family history of autonomic disorders.
- Post-viral onset: Viral infections may trigger or unmask underlying autonomic dysfunction.
Diagnosing Hypovolemic POTS
Proper diagnosis is essential to distinguish hypovolemic POTS from other subtypes and similar conditions.
Clinical Evaluation
A thorough review of symptoms and history, including the impact of standing, diet, hydration status, and any previous viral illnesses or surgeries.
Tilt Table Testing
This test evaluates heart rate and blood pressure response during changes in posture. In hypovolemic POTS, a significant heart rate increase occurs without a significant drop in blood pressure.
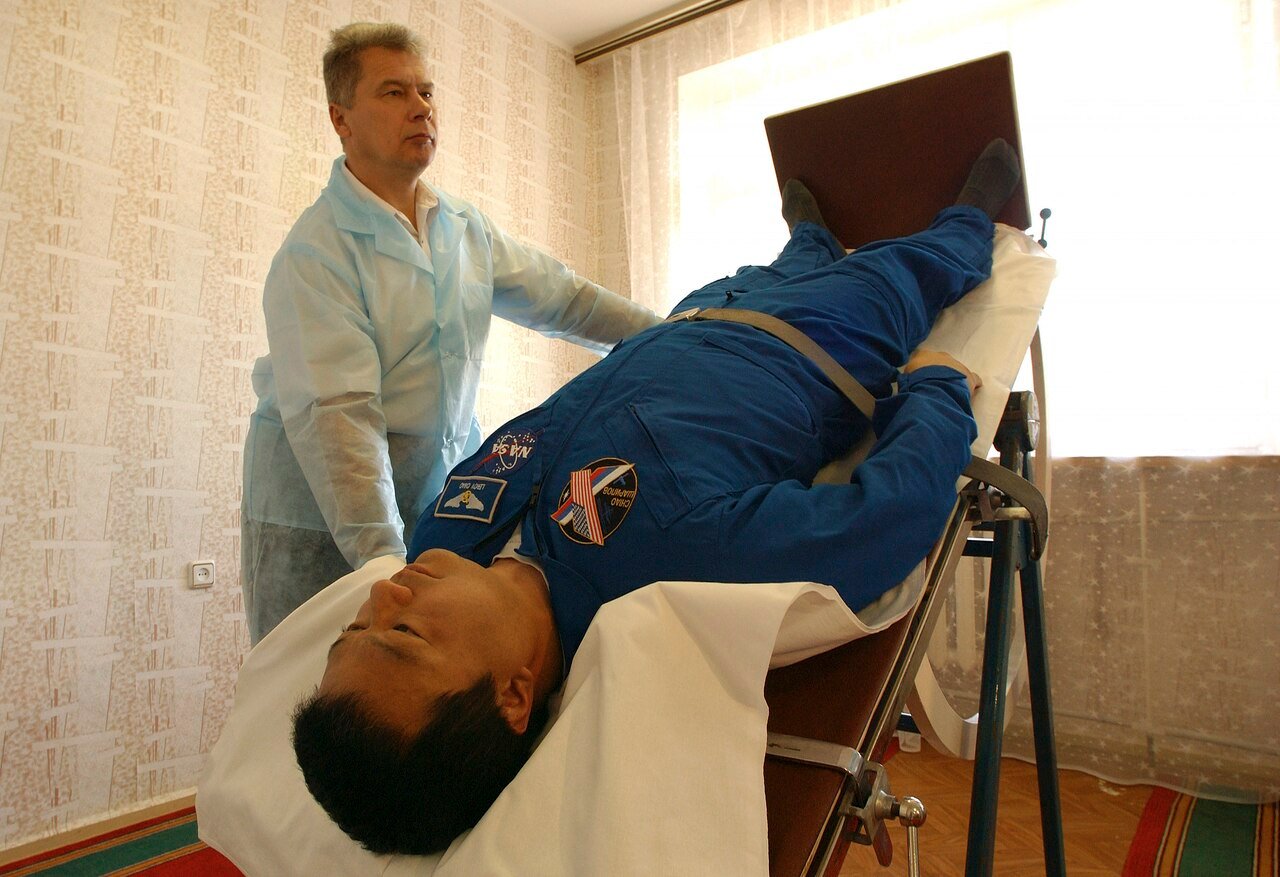
Blood Volume Studies
Specialized blood volume analysis can confirm low plasma volume.
Hormonal Tests
Assessment of RAAS hormones such as aldosterone and renin levels can identify hormonal imbalances contributing to hypovolemia.
Treatment and Management of Hypovolemic POTS
Effective management focuses on increasing blood volume and improving vascular tone.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Increased fluid intake: Aim for 2-3 liters of water daily.
- High salt diet: Intake of 3,000–5,000 mg of sodium per day is often recommended.
- Physical counter-maneuvers: Crossing legs or tensing lower muscles can help blood return to the heart.
- Recumbent exercise: Rowing, swimming, and recumbent biking are well tolerated.
- Compression garments: Abdomen-high compression garments reduce blood pooling.
Medications
- Fludrocortisone: Helps retain sodium and increase blood volume.
- Desmopressin (DDAVP): Reduces urine output and increases water retention.
- Midodrine: A vasoconstrictor that helps raise blood pressure and reduce pooling.
- Beta blockers: May help regulate heart rate in some cases.
Nutritional Support
A nutrient-rich diet supports overall health. Supplementation with magnesium, B vitamins, and electrolytes can help manage fatigue and orthostatic symptoms.
Living with Hypovolemic POTS and Dysautonomia
Living with hypovolemic POTS requires careful symptom management, consistency, and support.
Psychological Impact
Fatigue, brain fog, and exercise intolerance can affect mental health. Supportive therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness, and pacing strategies can make a difference.
Community and Advocacy
Engaging with organizations like Dysautonomia International, or online POTS forums, offers community support and access to research updates.

GnarlyTree | CONNECTED CONDITIONS
The POTS and MS Connection | Understanding Dysautonomia in Multiple Sclerosis
Understanding the Overlap Between Dysautonomia & Multiple Sclerosis Explore the POTS and MS connection, how dysautonomia overlaps with multiple sclerosis, and what it means for diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment strategies. Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)...
Frequently Asked Questions for Hypovolemic POTS
Is Hypovolemic POTS reversible?
Some patients experience symptom improvement with consistent treatment, though long-term management is often required.
How is it different from dehydration?
While dehydration can worsen hypovolemic POTS, the condition involves chronic low blood volume that persists even with adequate fluid intake.
Can I exercise with Hypovolemic POTS?
Yes, but it should be structured and gradual. Recumbent or horizontal exercises are best tolerated.
Conclusion
Hypovolemic POTS is a challenging yet manageable form of dysautonomia. It results from reduced blood volume and impaired vascular regulation, leading to hallmark symptoms of orthostatic intolerance. With an accurate diagnosis and a personalized treatment approach, many patients can regain functionality and improve their quality of life.
If you suspect hypovolemic POTS, consult a medical professional experienced in POTS and dysautonomia for a comprehensive evaluation.

Do you use compression garments daily?